Page 20 - Book6E
P. 20
Floor: the minimum interest rate of an ARM loan. This prevents an ARM loan from ever adjusting lower than the Start Rate.
Payment Shock: industry term to describe the upward movement of mortgage loan interest rates and its effect on borrowers. This is the major risk of an ARM, as this can lead to severe financial hardship for the borrower.
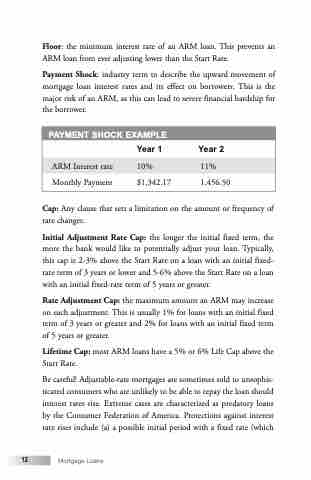
PAYMENT SHOCK EXAMPLE
Year 1 Year 2
ARM Interest rate 10% 11%
Monthly Payment $1,342.17 1,456.50
12
Mortgage Loans
Cap: Any clause that sets a limitation on the amount or frequency of rate changes.
Initial Adjustment Rate Cap: the longer the initial fixed term, the more the bank would like to potentially adjust your loan. Typically, this cap is 2-3% above the Start Rate on a loan with an initial fixed- rate term of 3 years or lower and 5-6% above the Start Rate on a loan with an initial fixed-rate term of 5 years or greater.
Rate Adjustment Cap: the maximum amount an ARM may increase on each adjustment. This is usually 1% for loans with an initial fixed term of 3 years or greater and 2% for loans with an initial fixed term of 5 years or greater.
Lifetime Cap: most ARM loans have a 5% or 6% Life Cap above the Start Rate.
Be careful! Adjustable-rate mortgages are sometimes sold to unsophis- ticated consumers who are unlikely to be able to repay the loan should interest rates rise. Extreme cases are characterized as predatory loans by the Consumer Federation of America. Protections against interest rate rises include (a) a possible initial period with a fixed rate (which